Our detailed assessment for Thursday, 17 March 2022
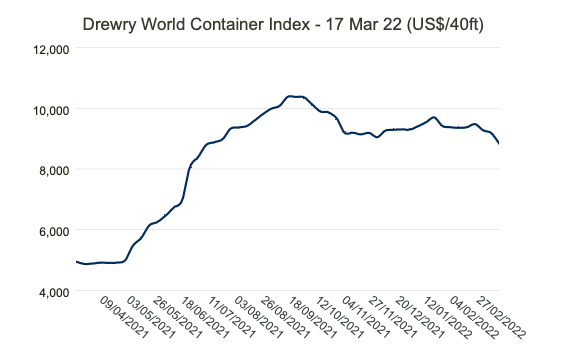
- The composite index decreased by 3.8% this week, but, remains 79% higher than a year ago.
- The average composite index of the WCI, assessed by Drewry for year-to-date, is $9,360 per 40ft container, which is $6,231 higher than the five-year average of $3,129 per 40ft container.
- Drewry’s World Container Index composite index decreased by 3.8% to $8,832.23 per 40ft container, but is 79% higher than the same week in 2021. The WCI composite index fell below $9,000 per 40ft container for the first time since 29th July 2021. Freight rates on Shanghai — Los Angeles sank 7% or $811 to $10,154 per 40ft box. Spot rates on Shanghai — New York dropped 5% or $685 to $12,276 per feu. Similarly, FAK rates on Shanghai — Rotterdam fell 4% or $464 to $12,221 per 40ft box. However, rates on Rotterdam — Shanghai grew 3% to $1,515 per feu. Rates on Shanghai — Genoa, Los Angeles — Shanghai and New York — Rotterdam rose 1% each and rates on Rotterdam — New York hovered around previous weeks level. Drewry expects spot rates to remain stable in the coming week.