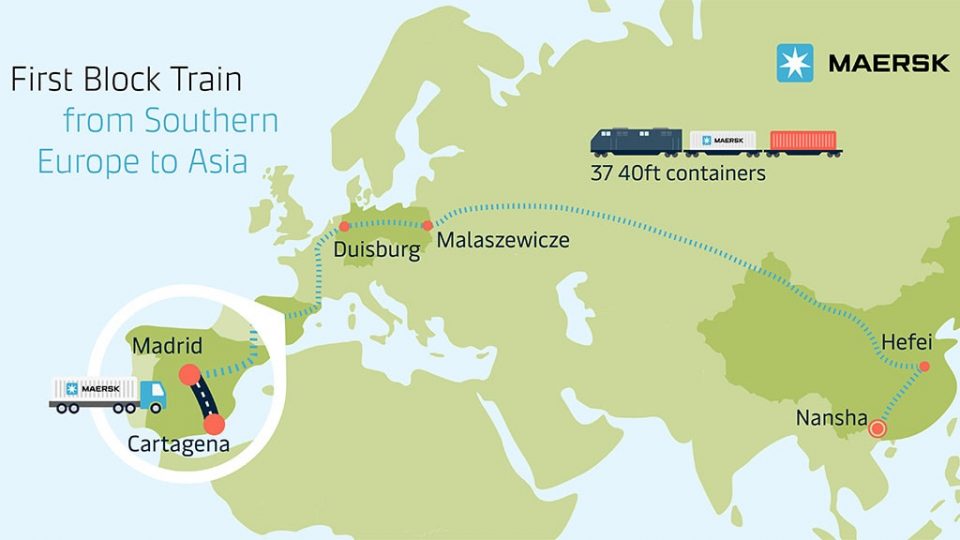
The service has a purely intermodal profile. During May, the cargo was transported by trucks from Carthagena, also in Spain, to Madrid. There, it onboarded the block train to Duisburg, crossed the EU borders through Małaszewicze and reached Hefei in China. From Hefei, it will reach Nasha by the end of June. The total travelling time will be 32 days in total, and the 37 40-foot container train carries chemicals.
More to come
Limited ocean capacities are the main driver for companies to turn to Eurasian rail. Especially when it comes to transporting chemical products, the cargo cannot afford delays. However, this type of transport also bears some complex characteristics, making the train to China even more successful, and paving the way for more similar services.
Indeed, the Spain-China connection worked quite flawlessly for Maersk. That is why the company already has another train from Spain to China in the pipeline. This time the train will head for Shanghai carrying 41 40-foot containers.