DB Cargo is responsible for running the service in cooperation with Mann Lines Multimodal, which operates the sea part between Kaliningrad and Oslo. UTLC ERA operates the rail route to Kaliningrad. The transported cargo consists of personal protection equipment and thus the fast transit times that the service offers are fundamental under the pandemic conditions. After all, compared to the traditional deep-sea transportation of these products, this link is approximately 30 days faster.
Tested route
Kaliningrad played a central role in Eurasian transportation during the past year. DB Cargo started using the Russian conclave port last April to provide alternatives to other frequently congested European entry points of the New Silk Road. Since then, more than 90 trains originating from Xi’an reached the port through which they linked to other European destinations.
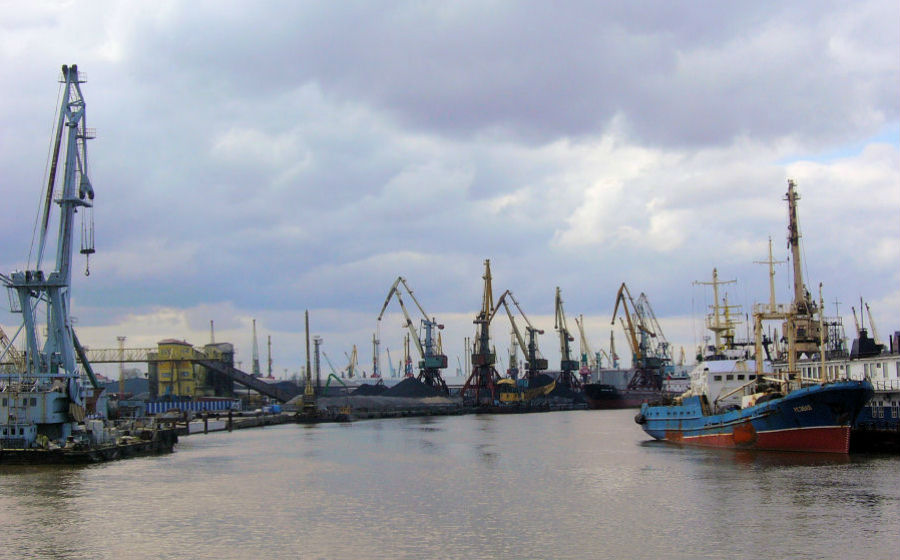

Port of Kaliningrad
Another significant development was also the connection of Kaliningrad with two German destinations-these of Rostock and Duisburg. With a maritime service accorded again by Mann Lines, the cargo was transferred from Kaliningrad to Rostock and then distributed in the European hinterland, utilising Duisburg’s hub function. The launching of this transit route was among the most important events regarding Eurasian transport in 2020.
Apart from that, Rostock was also used to transport products toward the Nordic countries via short sea services. Understandably, the cooperating companies have already gained needed experience in terms of multimodal transport, a fact that makes them more than suitable to undertake the connection between Oslo-Xi’an.
Norway’s role
On the other hand, the Nordic country is intensively trying to acquire its role in the New Silk Road. As part of the Nordic Railgate Cooperation project, Norway aims to connect with China through Finland and, further on, through the Russian Trans-Siberian route. The primary purpose for the participation in this route is the transportation of eatery goods such as salmon. Until now the transport of such goods takes place via air or sea.
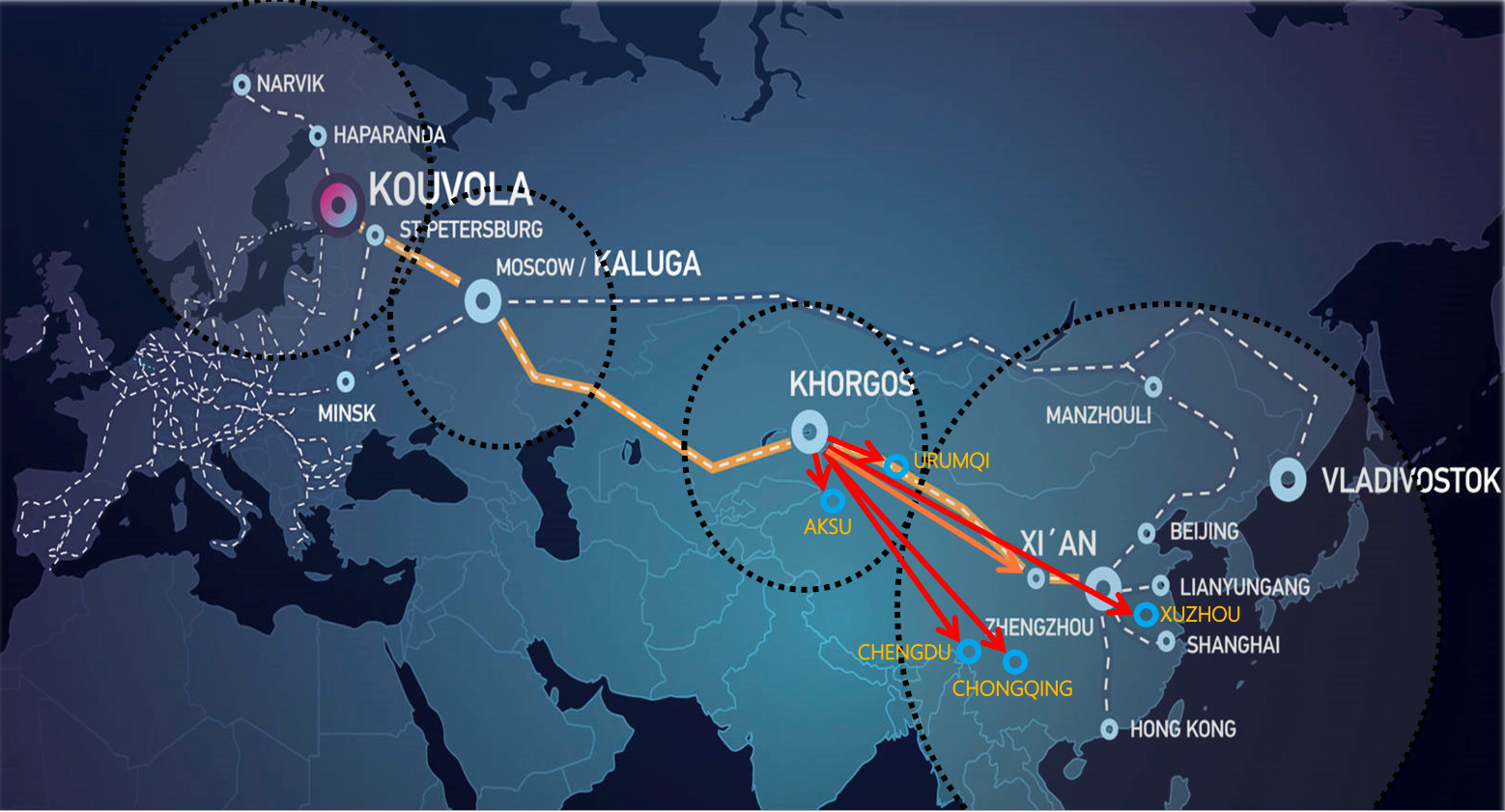
Map of Nordic route
On top of that, though, by linking to China, Norway can acquire a more notable role: that of completing the New Silk Road’s trip to the other side of the globe, specifically the US and Canada. With the addition of the country’s northern port, Narvik, in the map of destinations, there is a possibility to launch transatlantic links that will stretch from North America to the Far East. A very persuasive motive for such a development is the lack of congestions.
More possibilities
Similarly, Xi’an-Oslo’s new link, even though it is not using Scandinavian railways par excellence, could serve akin purposes. First of all, it can involve Nordic countries in Eurasian transportation more extensively. Secondly, it can shift specific products, as mentioned previously, to rail instead of other transport modes. Finally, it can still contribute to realising the goal of transatlantic shipping. By distributing cargo that arrives in Oslo, through Kaliningrad, to the rest of the country, it can easily reach ports such Narvik that can connect with the other side of the world.