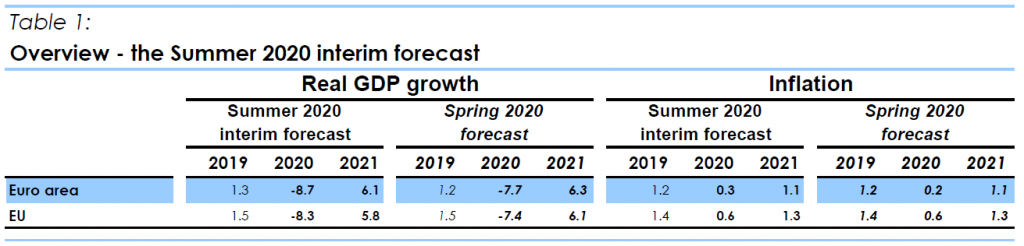
Overall, the euro area economy is forecast to contract by about 8.3% in 2020 before recovering at an annual growth rate of 6% next year. While economic disruptions have been broad based, first quarter data also confirmed the highly asymmetrical nature of the impact across countries and industries. For the second quarter, all screened indicators suggest an acceleration of the contraction in economic activity with persisting differences across countries and industries. Looking forward to the second half of the year and 2021, the European economy is expected to bounce back, but with bigger and more persistent differences across Member States than expected in spring. In Germany, the massive fiscal stimulus is expected to boost demand, so it is therefore expected to pave the way for a relatively swift recovery, starting in the second half of this year.
The impact has also been highly asymmetrical among industries. The sharpest declines were observed in trade, transport, accommodation and food services as well as arts, entertainment and other service activities (both at −6.8% q-o-q). Agriculture, forestry and fishing, together with financial and insurance activities saw the mildest declines (at −0.8%). Industrial production collapsed by 17.1% in April, resulting in a cumulative contraction of about 27% since February. The most affected industries were the manufacture of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers (about −70%), as well as that of leather and related products (around −60%) followed by clothing (around −40%). Most activities saw output contractions of between 15% and 25%.